Junos separated Routing and Forwarding plane
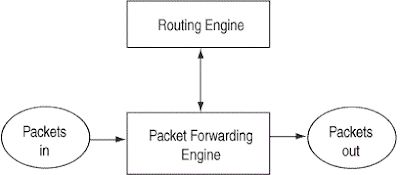
The M series Juniper routers are designed with separate route and forward architecture. This is a great design that can benefit some one in a production enviroment. The main bottleneck is the resource drain on the router and packet drops. With this design these errors are eliminated as they can be, forwarding plane will still forward packet despite the over utilized routing protocol operation. A logical diagram can clarify this architecture even more.
The routing engine is used to provide routing protocol service, similar to BGP, OSPF, RIP, IS-IS and other Layer3 traffic. Packets that are forwarded upon the routing protocol decisions are passed onto packet forwarding engine. The PFE engine caches the paeket flow and if no protocol control is needed it works independently of the RE. This is a good thing to know if some routing protocol fails we still have the basic packet flow.
To communicate PFE and RE use integrated links that can be controlled with firewall filters to drop the traffic that is not due to pass trough the link. This way the we prevent the over utilizing the router and freeing up some router resources with simple config scripts. Also the security is touched here, as the managament can be filtered through these links.
Control plane has a simple task of generating a routing table and creating the RIB (Routing information base) and FIB (Forwarding information base). Forwarding plane is responsible for simple packet forwarding. This packet forwarding is happening via hardware (ASIC). The path is from the ingress interface to the proper path selected egress interface.
This special infrastructure of the JunOS router has separated forwarding decisions from the MAIN cpu unit.This isolation of tasks no longer need help only from a single processor. This benefits network engineer in production environment. During the running time they can load new application modules without shutting down the router and no uptime is disrrupted. The JunOS introduces us with graceful restart capabilities.
The routing engine consists of:
This special infrastructure of the JunOS router has separated forwarding decisions from the MAIN cpu unit.This isolation of tasks no longer need help only from a single processor. This benefits network engineer in production environment. During the running time they can load new application modules without shutting down the router and no uptime is disrrupted. The JunOS introduces us with graceful restart capabilities.
The routing engine consists of:
- Intel based PCI platform (CPU) that is running JunOS
- SDRAM storage of the routing and forwarding tables
- Compact flash storage for platform images
- Hard disk for a secondary storage
The Routing engine has a 100 Mbps link to the Forwarding engine. PFE has a design of Fabric switch implementation features. On the other hand JunOS has a very well designed virtuelized router implementations, that allows network engineers to have multiple instances of router inside a single hardware.
All together I will introduce more JunOS features in future blogs.
Feel free to comment.
No comments:
Post a Comment